

Do you know the working principle and precautions of centrifuge?
Centrifuge uses an efficient separation technology, widely used in pharmaceutical, chemical, food and other fields. The centrifuge separates the mixture by utilizing the different sedimentation coefficients of materials under different centrifugal forces to obtain the target product. It has important applications in the preparation of biological products, separation of suspensions and other processes. The full centrifuge process can be divided into pre-treatment, centrifugal separation and post-treatment, and each link has unique process requirements and technical difficulties. Now we will take you to deeply understand the centrifuge...
What are the application scenarios of centrifuges?
1. Application of centrifuges in hospitals: Centrifuges in hospitals are mainly used for separation and purification of blood, such as plasma separation, platelet separation, serum and serum separation and plasma purification.
2. Application of centrifuges in the food industry: Centrifuges can be used for the extraction of fruit and vegetable juices, and can also be used for the separation of milk powder in the dairy or dairy product manufacturing industries.
3. Application of centrifuges in the chemical industry: Centrifuges can be used for the concentration, recrystallization, and impurity removal of chemical substances.
4. Application of centrifuges in water treatment industry: centrifuges can be used for wastewater recycling, refining of recycled water, cleaning and protection of water treatment facilities, etc.
5. Application of centrifuges in mud treatment industry: centrifuges can be used for oil field mud deoiling, cleaning and recycling of sewage treatment facilities, mud preparation and dilution of precipitants, etc.
What types of centrifuges are there?
1.Separation centrifuge: Separation centrifuge is the most widely used type of centrifuge, mainly used to separate solids from liquids or different types of solids in a mixture. Common applications include solid-liquid separation, solid particle classification, protein extraction, blood component separation, etc.
2.Speed centrifuge: Speed centrifuge refers to a centrifuge with a relatively high working speed, which can reach tens of thousands of revolutions per minute. It is mainly used to separate small particles or samples with small molecular weight, such as sedimentation centrifugation of nucleic acids and proteins.
3. Ultra-high-speed centrifuge: Ultra-high-speed centrifuge is a type of speed centrifuge. The working speed can reach hundreds of thousands of revolutions per minute. It is mainly used to separate microparticles, ultrafine particles, viruses and other samples. Common applications include separation of virus particles, protein crystallography research, etc.
4.Continuous centrifuge: Continuous centrifuge is a centrifuge that can work continuously and is suitable for large-scale centrifugal separation, such as separation and dehydration processes in industrial production.
5. Process centrifuge: Process centrifuge is a large centrifuge specially designed for industrial production. It can perform large-scale centrifugal separation, concentration, dehydration and other process operations. It is widely used in chemical, food, pharmaceutical and other industries.
Of course, in addition to the above types, there are also cantilever centrifuges, inclined disc centrifuges, jet centrifuges, variable volume centrifuges and other types for the separation of different biological substances.
What is the working principle of the centrifuge?
I. Separation of particles in liquid under gravity
When the liquid containing particles is left to stand for a period of time, the particles in the liquid are affected by gravity, and the heavier particles sink and separate from the liquid. This phenomenon is called gravity sedimentation.
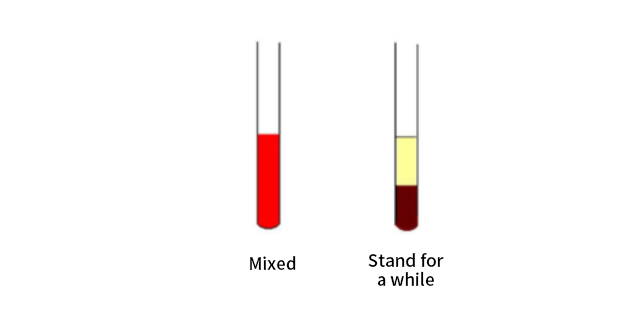
The speed at which the particles sink is related to the size, shape, density, strength of the gravity field and viscosity of the liquid.
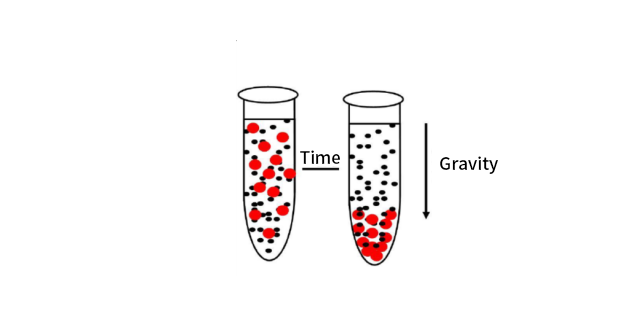
II. Basic working principle of centrifuge
In the centrifuge, the centrifuge tube is placed in the centrifuge rotor. When the centrifuge is turned on, the centrifuge tube rotates around the axis of the centrifuge rotor and moves in a circular motion. The sample particles in the centrifuge tube will also move.
If the particles are in a vacuum, the particles will fly in the tangential direction. This tangential motion of particles in circular motion is called centrifugal sedimentation.
In fact, the particles are moving in the medium. When the particles move tangentially, they will move in a curve in the centrifuge tube due to the friction resistance of the medium. The greater the resistance of the medium, the smaller the sedimentation speed of the particles and the shorter the sedimentation distance. The greater the rotation speed, the faster the particles will settle.
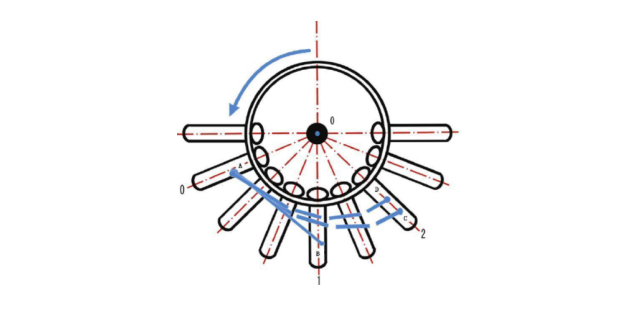
Working principle of centrifuge
When the acceleration in the centrifugal field reaches tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of times the acceleration of gravity, the sedimentation of particles is also accelerated by the same multiple. In this way, many fine particles that cannot settle in the gravitational field and components of objects with low density can be separated and purified by centrifugal technology.
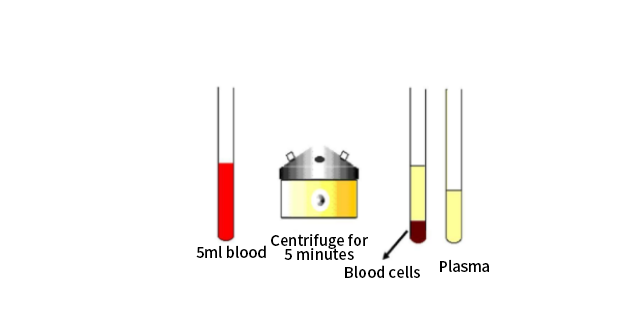
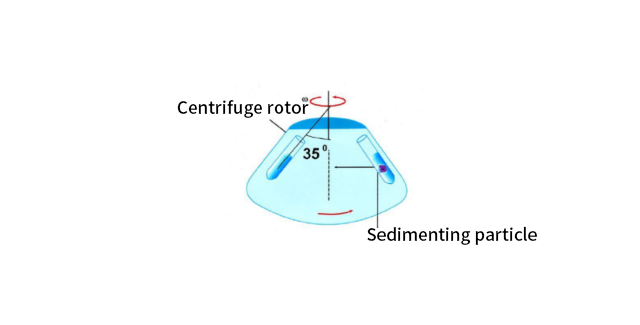
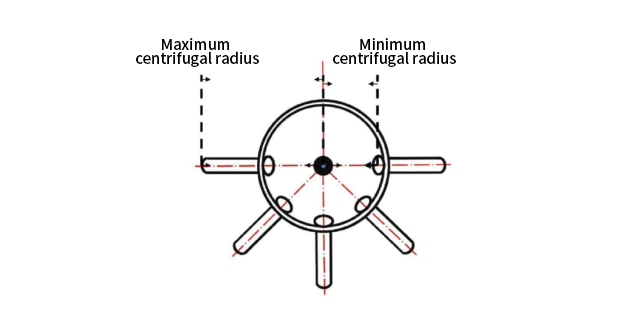
When the centrifuge is running, the centrifuge tube is at a certain angle to the rotating axis of the rotor. The centrifuged sample solution is placed in the centrifuge tube. The distance from the top of the centrifuge tube to the center of rotation is different from the distance from the bottom of the centrifuge tube to the center of rotation. Therefore, the centrifugal field borne by the top and bottom is also different.
The distance from the top of the centrifuge tube to the center of rotation is usually called the minimum centrifugal radius r min, and the centrifugal field borne there is the minimum centrifugal field; the distance from the bottom of the centrifuge tube to the center of rotation is called the maximum centrifugal radius r max, and the centrifugal field borne there is the maximum centrifugal field.
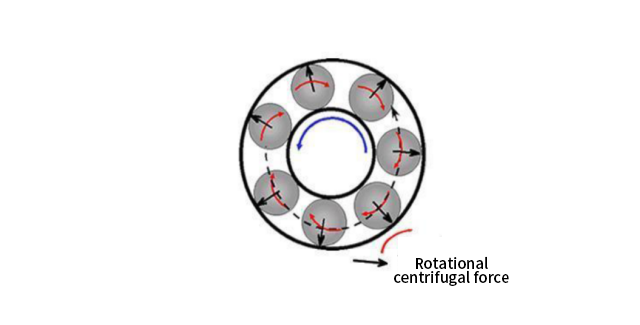
1. Centrifugal force
When the external force on an object is less than the centripetal force required for movement, the object will move away from the center of the circle. The phenomenon of an object moving away from the center of a circle is called centrifugal phenomenon, also known as centrifugal motion. Centrifugal motion is caused by the disappearance or insufficiency of the centripetal force.
2. Relative centrifugal force (RCF)
Relative centrifugal force refers to the centrifugal force acting on particles in a centrifugal field, which is equivalent to a multiple of the earth's gravity. The unit is gravitational acceleration "g"
3. Sedimentation velocity
Refers to the distance a substance moves per unit time under the action of a strong centrifugal force.
4. Sedimentation time
The time required for a certain solute in a solution to settle and separate at a certain speed of the centrifuge.
5. Sedimentation coefficient
The sedimentation velocity of particles under the action of a unit centrifugal field. The sedimentation coefficient is related to the molecular weight, molecular density, composition, shape, etc. of the sample particles. The greater the mass or density of the sample particles, the greater the sedimentation coefficient it exhibits.
What else do you need to pay attention to after understanding the above content?
I. Safety precautions
1. Before using the centrifuge, be sure to be familiar with the instrument's operating instructions and operate it correctly according to the instructions. Pay attention to the maximum speed and maximum capacity limits of the centrifuge.
2.When using the centrifuge, wear safety glasses, laboratory gloves and lab coats to prevent accidental injuries caused by sample splashing or instrument failure.
3.The centrifuge will generate loud noise and vibration when running, so the centrifuge should be placed on a stable laboratory table to ensure its stable operation.
II. Sample preparation and operation precautions
1.The sample should be placed as evenly as possible in the centrifuge rotor to ensure uniform centrifugal force. At the same time, the centrifuge rotor also needs to be balanced to avoid vibration or noise caused by imbalance.
2.The capacity of the centrifuge rotor is usually limited, so when choosing a centrifuge tube or centrifuge cup, it is necessary to make a reasonable choice based on the volume of the sample to avoid exceeding the carrying capacity of the centrifuge.
3.The speed of the centrifuge should be reasonably selected according to the nature of the sample and the purpose of centrifugation. If the speed is too high, the sample precipitation may be lost or the centrifuge tube may rupture; if the speed is too low, the sample cannot be effectively separated.
4.The temperature of the centrifuge rotor also needs to be paid attention to. Generally, it should be kept at room temperature for operation. If the sample needs to be centrifuged at low temperature, a cooling device can be used in the centrifuge or placed in a refrigerated centrifuge.
III. Processing after centrifugation
1.After centrifugation, turn off the power of the centrifuge first, and wait until the centrifuge stops rotating completely before opening the centrifuge cover to avoid sample splashing due to rotor rotation.
2. After opening the centrifuge cover, carefully remove the centrifuge tube or centrifuge cup to avoid collision or dumping the sample.
3.For the samples after centrifugation, we need to pay attention to separating the supernatant and the precipitate, and perform corresponding treatment. If the sample needs to be preserved, it should be stored according to the experimental requirements to avoid sample deterioration or contamination.
As a commonly used experimental instrument, when choosing a centrifuge, we must select an appropriate centrifuge according to the results that the sample needs to achieve. We also need to pay special attention to safety when using it and follow the operating procedures to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the experiment. In 2023, Zhongke Meiling launched a -20~40℃ high-speed centrifuge with a speed range of 500r/min to 18500r/min and a centrifugal force of up to 32531xg. It is suitable for university laboratories, inspection departments, scientific research institutes and other institutions. After more than a year of market verification, Zhongke Meiling centrifuge CT-G185R has received unanimous praise from users and has now completed CE certification to meet the needs of global users.

In 2024, we will launch the new arrival CT-G175R . This product will be exhibited at the 56th Medica Exhibition in Düsseldorf, Germany in 2024. Its launch will bring greater surprises to everyone. If you want to know the details in advance, please visit : (https://www.melingbiomedical.com/). We also look forward to meeting you at the MEDICA exhibition and taking you to experience the high-precision centrifugal speed control technology of Zhongke Meiling high-speed centrifuge that far exceeds the national standard.
